NCDs are non-communicable diseases also known as chronic illnesses that are long-term in nature. They have no proper cure, are progressive and life limiting. Additionally, NCDs are terminal illnesses that can lead to death.
There are many factors that cause NCDs; the studies have shown that NCDs are as a result of a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioral factors. Aging is also thought to increase the possibility of getting chronic illnesses due to low immunity.
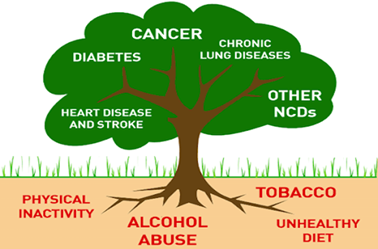
Poverty is closely linked with NCDs. The rapid rise in NCDs is predicted to impede poverty reduction initiatives in low-income countries, particularly by increasing household costs associated with health care. In low-resource settings, healthcare costs for NCDs quickly drain household resources. Common NCDs include cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, diabetes, cancer, chronic kidney diseases etc. those who have other underlying condition like HIV are at a higher risk.
A way of reducing these NCDs is by Reducing the risk factors associated with these diseases like tobacco and alcohol consumption, lifestyle modification, eating right foods and at the right times, adapt health-seeking behavior, do physical exercises, avoid stressing moments and seeking for help when stressed or anxious. Annual medical check-ups can help detect and treat NCDs before they become chronic.

